In the last blog post, I’ve discussed co-occurrence and its importance in your search engine optimization process. Co-citation often discussed together with co-occurrence, is another advanced hot SEO topic that represents the link-building relationship between sites.
Co-citation: An Overview
Before knowing what exactly co-citation is, we should know about citations.
A citation is a reference to a published or unpublished source. Simply put, it means a direct mention of your business or brand on the web.
Co-citation is defined as the frequency with which two documents are cited together by other documents. If at least one other document cites two documents in common these documents are said to be co-cited. The more co-citations two documents receive, the higher their co-citation strength, and the more likely they are semantically related.
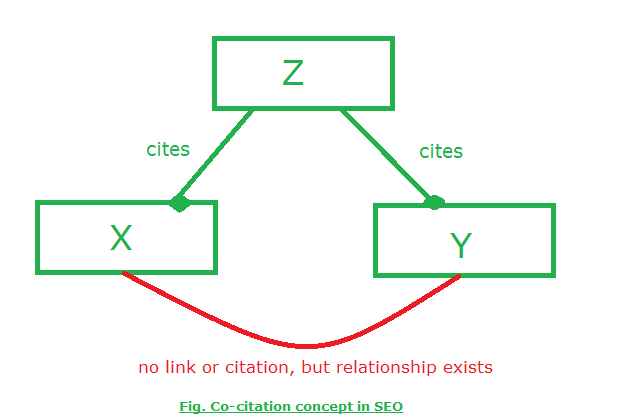
Let’s understand this with help of an example. If an article (X) and article (Y) are cited by a website (Z), then articles X and Y are said to be in a co-citation relationship.
So, there will be three relationships – Z&X, Z&Y, and X&Y. While there is no direct link between X and Y, but Z links both of them, then X and Y will be in a relationship due to the co-citation principle.
If X is a more authoritative website, then it will affect Y in a more positive way. This is called the transitive effect of co-citation.
Practical Tips to Implement Co-citation in Your SEO Strategy
Below are few tips that will help you know how to use co-citation in your search engine optimization strategy.
1. Link to Highly Relevant and Authoritative Sites
Since co-citation is a relation between links (or brand name), this becomes more important to link to only what is relevant and of high quality.
Think about Wikipedia, world’s largest online encyclopedia and hub of informative and authoritative links. Try adding high-quality, informative and authoritative citations similar to it.
It’s good to mention all relevant references in your content to increase the trust and authority of your published content. When you add quality links to your website, the transitive effect of co-citation give your page an SEO benefit.
2. Don’t Link to Poor Sites
Poor sites (which lacks in trust, relevancy, authority and high-quality content) can ruin your search presence, plus, they will make your page out of calculation towards building authority and rank in Google. Again, the transitive effect will be there to hurt your page, if you link to a poor or bad site.
3. The Words Around Your Link Matter (Co-occurrence)
In recent time, co-citation has been used interchangeably with co-occurrence. They are related but both terms are actually different in meaning.
Co-occurrence is about the relationship between words, on the other hand, co-citation is clearly about links. However, both can be incorporated into your SEO strategy, especially in link-building together to get better results.
There is an evidence that the rich-anchor texts are more influential than any other type of keywords. But, modern SEO and Google’s latest and smarter updates such as Hummingbird and Penguin have made the scenario different.
By using brand keywords, related terms, synonyms and long-tail keywords, Google can reward you in search results. Using relevant terms and keywords around your link will make your content and link profile more natural.
Conclusion
When your website is mentioned (not necessarily linked) by many different sources, with the help of co-citation, its authority is established which may help it rank higher in search engine results.
This can also help you overcome competitors who have a good and well-optimized content but lacks citations over the web.
What are your thoughts on co-citation? I’d love to hear you all in the comments below.




 How To Start a Career in SEO: 8 Easy Steps
How To Start a Career in SEO: 8 Easy Steps